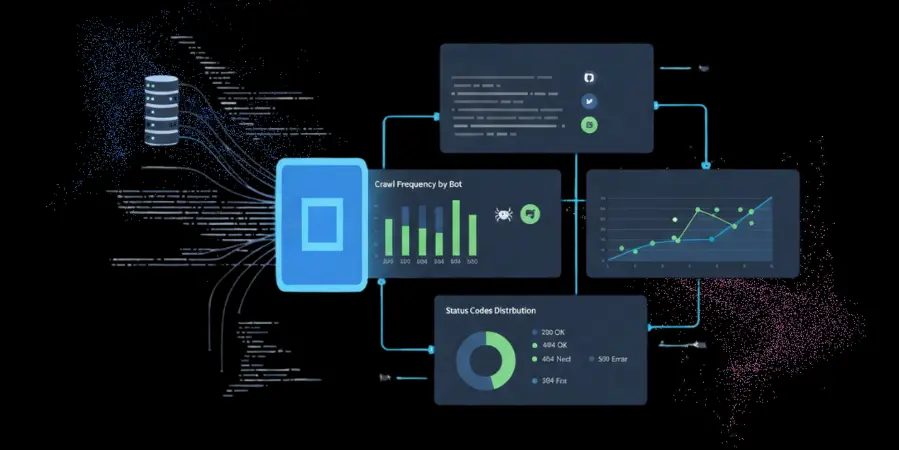
The analysis of advanced log files gives SEO companies information about how search engine bots explore a site beyond what is available to them from standard SEO software programs. Analyzing server log files will allow an SEO company to investigate crawling problems, indexation issues, and opportunities for optimization that contribute to improving a website’s organic performance. In this blog, let’s learn more about advanced log file analysis for SEO for various analytical purposes and troubleshooting.

What is an Advanced Log File?
A log file is similar to a detailed journal for computers, documenting each interaction a user or other entity has with a system. Log files can collect many different types of activity within an operating system/application/server, and they will record the sequence of these activities (events) along with date/time stamps. This information can be used for a variety of different types of analysis and troubleshooting activities.
Importance of Log File Analysis in SEO
Analyzing log files is a crucial element in optimizing search engine optimization (SEO). For example, log file analysis allows you insight into how search engines view your website. The analysis of logs will offer you an insight into each visit from crawlers that gives you the ability to make changes to the structure of your website and the way in which your content is displayed in order to get the best indexing possible by Google and other search engines. The technical SEO audit is performed as a way to improve the effectiveness of individual websites with respect to search engines.
Key Elements of Log Files
The majority of the content of log files consists of a list of entries describing each HTTP request made to the web server. Each Log file will typically contain a very large amount of information, the essential components of which would be the following core components of the log entry:
1. URL Path:
The URL address of the requested resource on your website.
2. Query String:
Optional additional data you may have attached to the URL (this could include search parameters or a tracking code).
3. User-Agent:
This is the software application (usually a web browser or web crawler) that made the request.
4. IP Address:
Each requesting device has a unique numeric identifier (address) assigned to it and may have a relationship to the physical location of that device.
5. Timestamp:
It is the exact date and time when the web server received a request.
6. Request Type:
Determines whether the request was made using the GET method (used to request that a user receive data) or the POST method (used to send data to a web server).
7. HTTP Status Code:
The response provided by the web server to the originating request. This will vary, with different codes designating success, redirection, client error, or server error.
Knowing the components of a log file is important to fully understand the analysis because they will not only show you how visitors are using your site, but they will also show you how you may improve the web experience for users.
Process for Effective Log File Analysis
Below are the steps to follow for effective log file analysis:
Step 1: Gather Log Data
Begin by pulling all logs from your web servers and any applications or systems that you might have. By using an automated tool, you can centralise your data in one place, ensuring continuous data collection and log storage for accurate and continuous analysis.
Step 2: Break logs into Pieces
Break the raw log file data into a structured format. This includes dividing the raw log file into individual elements such as IP address, timestamp, URL, and user agent. Good log file parsing allows for elements to be filtered, sorted, and analysed much more easily.
Step 3: Reviewing the Data
Once you have parsed the log files, you can go through the log files to see what crawl patterns exist for the search engine crawl, what errors, anomalies (i.e., the same user accessing the site more than once in one day), and performance issues occur. The results of this step will help you to better understand your users’ behaviours on your site, your systems’ health, and the activities of search engine bots.
Step 4: Visually show findings
Dashboards, charts, and graphs can simplify complex data and allow you to visually see trends, problem areas, and key metrics at a glance.
Step 5: Fix the Problems
Use your findings to make changes to fix errors, improve crawl efficiency, and adjust your website to optimize performance. Continue to monitor the results of your changes regularly, and continue to go through this process periodically to maintain your ongoing SEO improvements.
Key Insights Acquired
Analysing Crawl Patterns and Frequency:
An analysis of the logs from user activity on a website reveals how regularly (and how thoroughly) a search engine bot will visit different pages within that same site. This analysis is helpful to determine both the most crawled pages compared to the least crawled, which relates to both the relative importance of these pages and to identifying potential issues such as accessibility problems, internal linking issues, or poor content quality.
Identifying Indexability and Redirect Issues:
In addition to providing insights into which pages are frequently or rarely crawled, analyzing server logs can help identify factors that negatively affect page indexing, such as crawl error codes, broken links, and inefficient redirects. An analysis of the log files will also provide insight into issues such as 302 redirect errors, redirect chains, and trailing slashes that waste crawl budget and negatively impact a page’s search engine ranking. Once identified, these issues can be addressed to enhance overall search visibility.
How Log File Analysis Improves SEO Performance
Enhancing User Experience and Site Performance
Log analysis identifies any slow page load times, server errors, and technical issues that could be negatively impacting the performance of your site. By resolving these issues, you will improve the site’s crawlability, improve your users’ experience when using your site, and increase their engagement with your site (and thus, ultimately increase conversions).
Effective Use of Crawl Budget
By analysing logs, you can easily eliminate crawl time spent on low-value web pages and redirect search engine bots to valuable pages on your site. This will allow your site to discover new content and index that content more quickly, and be ranked more highly by the search engines for those key pages.
Overcoming Challenges Commonly Associated With Log File Analysis
Large Volumes of Data
Log files can be truly enormous and incredibly complicated. Using efficient storage technology, good data compression techniques, and log-management tools or Big Data technology will help process your data more quickly. You can also reduce the amount of “noise” in your log files by focusing on only the relevant fields of each log entry, and still keep key insights.
Limitations of Indexing and Classification
Slowness of index creation and improperly classified logs will usually be a hindrance during the analysis process. Using free-text search methods, smart tagging, and structured categorization will give you much quicker access to important data and provide better SEO insight from your analysis.
Takeaway
Log File Analysis for SEO helps an SEO agency have a better understanding of how well search engines are able to crawl and index the site. Agencies can then create strategies to maximize their chances of being indexed and improve search rankings by optimizing crawls, fixing technical issues, and improving site performance. These strategies will lead to improved search engine results, better user experience, and more measurable growth in an organization’s SEO.